Study 1
Study type:
Randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial
Purpose:
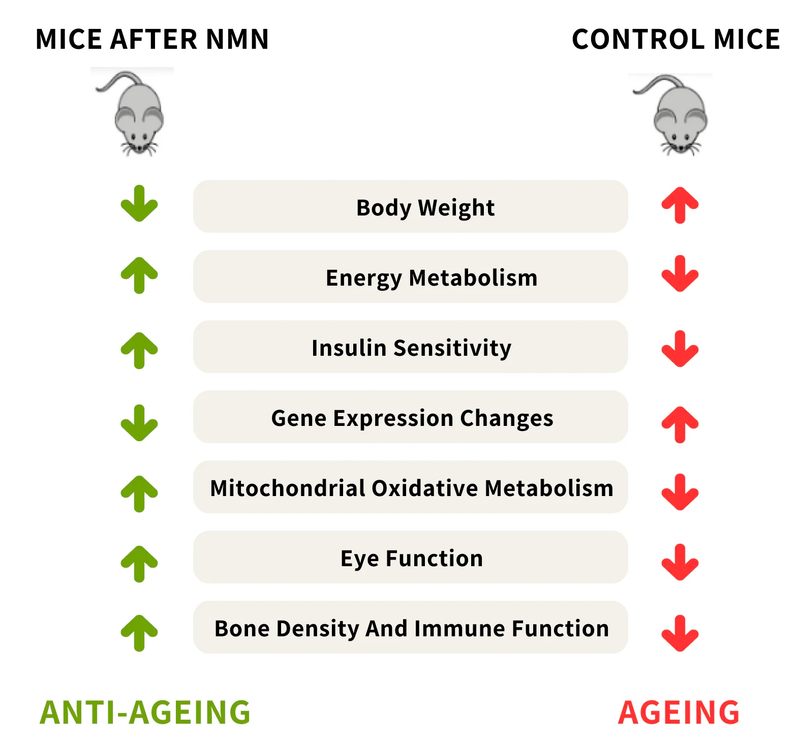
To evaluate whether chronic NMN supplementation elevates blood NAD+ levels and affects physiological dysfunctions in healthy older participants. NAD+ is a critical molecule that supports energy production, DNA repair, and cellular communication.
NMN dose:
250 mg/day or a placebo
Duration:
6 or 12 weeks
Participants:
42 men aged over 65 years
Results:
Long-term NMN supplementation was well tolerated and caused no significant adverse effects. Blood analyses revealed significant increases in NAD+ and its related metabolites concentrations, which play crucial roles in processes associated with energy production and tissue repair Research has found that NAD+ levels naturally decline with age, and an increase in NAD+ may enhance energy metabolism, support cell and tissue repair, and contribute to overall well-being.
The researchers observed significant improvements in muscle performance like grip strength and walking speed. It is worth noting that reductions in strength are a clinical indicator of ageing.
The authors concluded that long-term NMN supplementation may be used to boost NAD+ for preventing age-related muscle dysfunctions in humans.
Year:
2022
Link: